Whatsapp/Wechat:+86 13676922906
Achieving optimal stability in jaw crushers is critical for maximizing productivity, minimizing downtime, and ensuring operator safety. When processing abrasive or unevenly sized materials, unstable operations can lead to excessive wear, component failure, and reduced efficiency. To address these challenges, several interconnected approaches must be implemented, focusing on mechanical design, operational parameters, real-time monitoring, and proactive maintenance.
First, the foundation of crusher stability lies in robust mechanical construction. Modern jaw crushers utilize reinforced frames, heavy-duty eccentric shafts, and precision-machined bearings to withstand high-impact forces. However, even the most well-built machines require proper installation and alignment. Uneven foundation settling or misaligned components create uneven stress distribution, leading to abnormal vibrations. Installing anti-vibration mounts and regularly checking frame levelness using laser alignment tools can significantly reduce harmful oscillations. Additionally, selecting appropriate liners—such as those made from manganese steel with optimized tooth profiles—ensures consistent material grip and reduces slippage-induced instability.
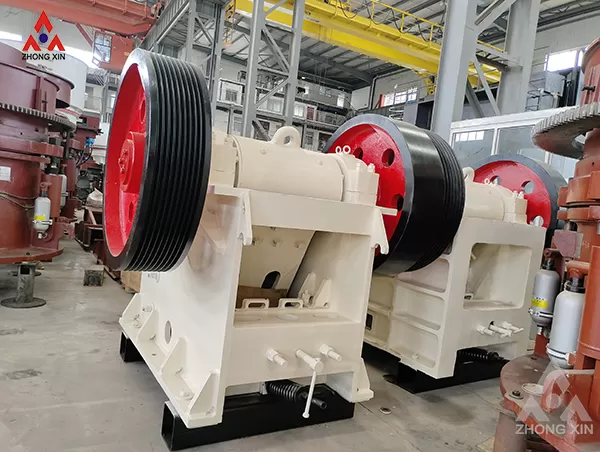

Second, controlling feed characteristics plays a vital role. Irregularly shaped or oversized rocks cause sudden load fluctuations, destabilizing the crushing chamber. Pre-screening materials through grizzly feeders removes fines and ensures uniform particle size distribution. For sticky or moist ores, installing heated vibrating pans prevents bridging and maintains steady flow rates. Automated systems that adjust feeder speed based on real-time power draw help balance throughput with machine capacity, avoiding both underloading (causing chatter) and overloading (inducing stall).
Third, dynamic balancing of moving parts minimizes inherent vibration sources. Eccentric weights on flywheels generate cyclic forces; if unbalanced, these resonate with structural modes, amplifying shakes. Annual dynamic balancing checks using portable sensors identify deviations early. Similarly, replacing worn pitman arms or toggle plates promptly prevents erratic motion patterns. Lubrication systems also contribute—automated grease pumps delivering precise quantities at scheduled intervals keep bushings and bearings operating smoothly, reducing friction-related jerks.
Fourth, advanced monitoring technologies enable predictive intervention. Mounting accelerometers on critical points captures vibration spectra; AI algorithms analyze frequency signatures to detect emerging issues like loose bolts or cracked cheekplates before failure occurs. Hydraulic adjustment systems allow quick closed-side setting modifications without stopping production, adapting instantly to changing rock properties. Some models integrate load cells measuring actual crushing force, feeding data into control units that automatically regulate feed rate or apply counter-pressure.
Fifth, routine maintenance forms the backbone of sustained stability. Daily inspections should include checking tension rod spring pressure, tightening all fasteners, and inspecting welds for cracks. Weekly audits might involve measuring oil temperature differentials across coolers—abnormal spikes indicate internal friction problems. Seasonal deep cleans remove built-up debris around pivot points, preventing binding. Keeping detailed logs of maintenance actions allows correlation with performance metrics, revealing hidden correlations between specific tasks and long-term reliability gains.
Finally, operator training bridges theoretical knowledge with practical application. Personnel who understand how settings affect stability—like increasing nip angle for harder rocks versus decreasing it for friable ones—make informed decisions. Simulator training prepares crews for emergency scenarios, emphasizing quick responses to unusual noises or movements. Encouraging open communication where frontline workers report subtle changes fosters a culture of prevention rather than reaction.
In conclusion, achieving stable jaw crusher operation demands a holistic approach combining engineering excellence, smart technology adoption, meticulous upkeep, and skilled human judgment. By treating each potential instability factor systematically—from foundation preparation to final product discharge—mines and quarries can unlock higher yields, extend equipment lifespans, and create safer working environments. The path forward involves continuous improvement: leveraging digital tools while never underestimating the value of hands-on expertise accumulated through generations of industry practice.
 Online Ordering
Online OrderingPlease complete the form below with your contact information and product requirements. We will get in touch with you as soon as possible—thank you for your cooperation!